But the inventory values and net income figures can vary significantly between periods as inventory levels and production volumes fluctuate. This causes net income to fluctuate between periods under absorption costing. Companies using absorption costing must understand these inventory valuation implications for accurate financial statement analysis when production volumes change.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Absorption Costing Method
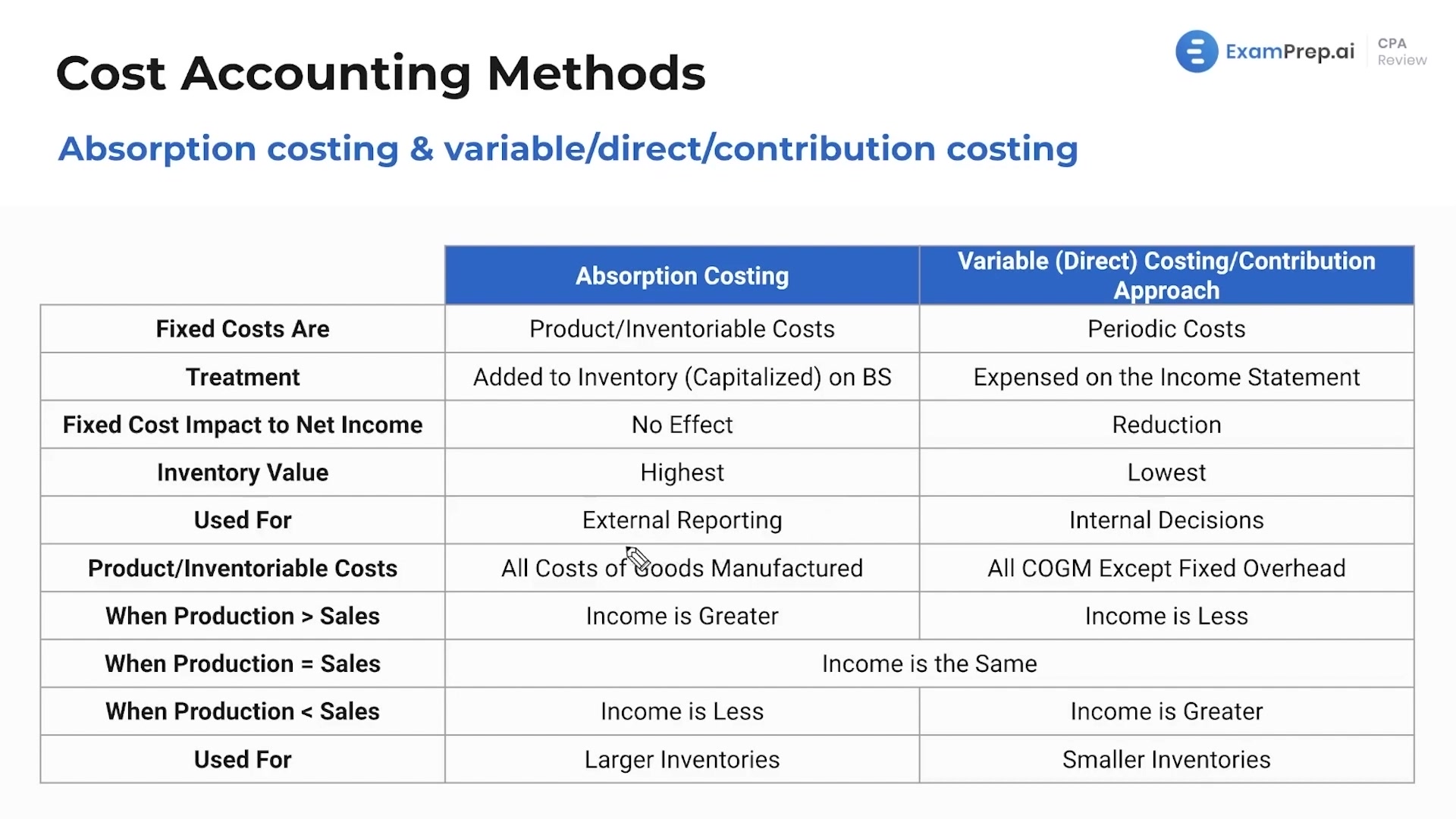
Variable selling andadministrative expenses are not part of product cost under eithermethod. Absorption costing, alsocalled full costing, is what you are used to under GenerallyAccepted Accounting Principles. Under absorption costing, companiestreat all manufacturing costs, including both fixed and variablemanufacturing costs, as product costs.
Income Statements:
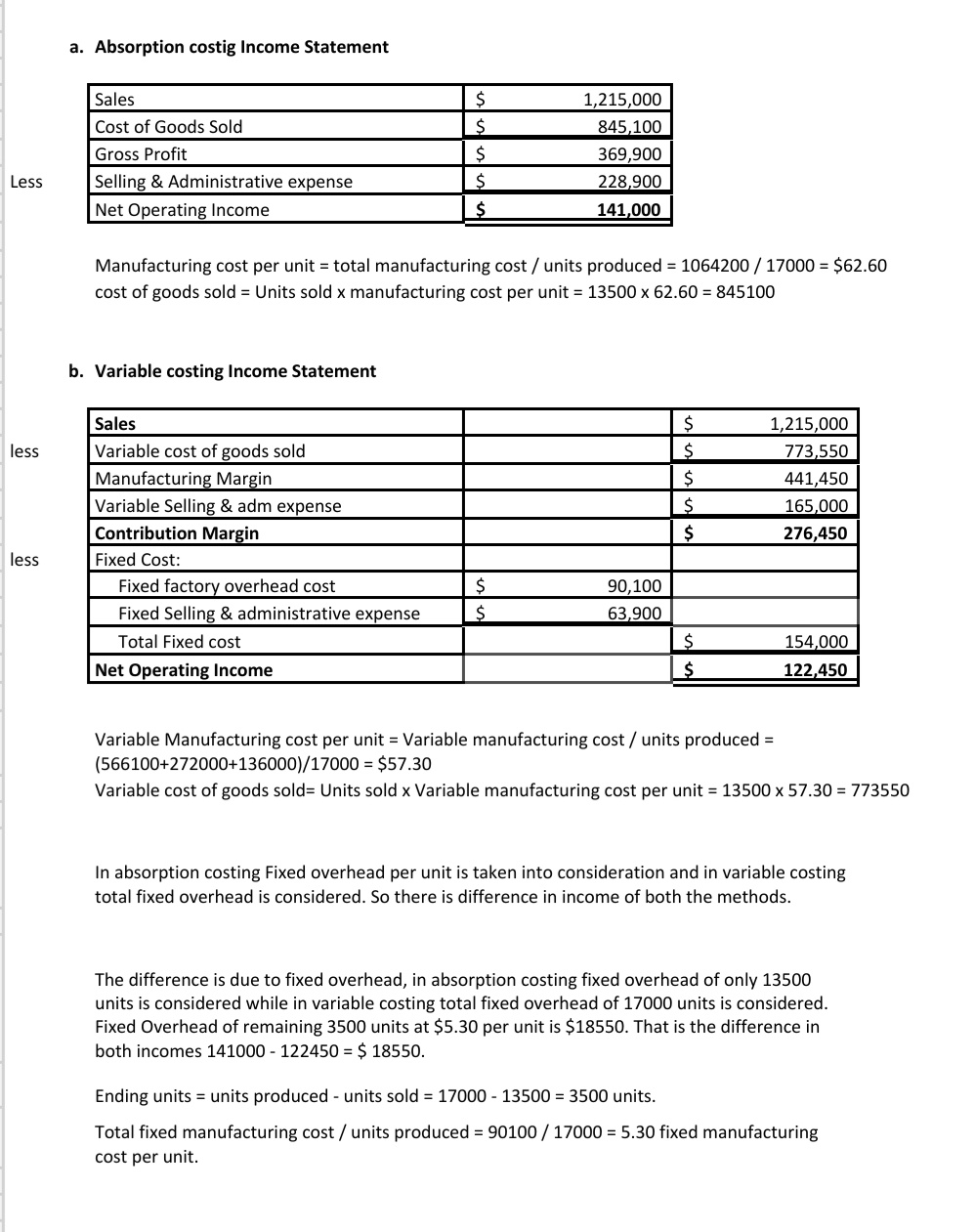
Here, we are going to discuss the income statement under absorption costing and see how the net profit differs. Before we look at the income statement, let us have a look at what absorption costing is. The basic format is to simply show the sales less the cost of goods sold equal gross profit. And also show the gross profit less the selling and administrative expenses and that equals the operating income.
Inventory Management with Absorption Costing
Variable costing also reports all expenses made with a period as a single item different from the cost of goods sold or still available for sale. Generally, absorption costing has to do with situations that affect the manufacturing costs of companies. It includes all product costs, which are both fixed and manufacturing product costs.
- Absorption costing is a method of costing that includes all manufacturing costs, both fixed and variable, in the cost of a product.
- Both fixed and variable operating expenses incurred during the period are recorded.
- Absorption costing states that every product has a set overhead cost, regardless of whether it is sold or not during a certain period.
What are the Differences Between Balance Sheet and Income Statement?
Absorption costing captures all manufacturing costs, including direct materials, direct labor, and both variable and fixed overhead, in the valuation of inventory. It’s important to note that period costs are not included in full absorption costing. In other words, a period cost is not included within the cost of goods sold (COGS) on the income statement. Instead, period costs are typically classified as selling, general and administrative (SG&A) expenses, whether variable or fixed.
The most basic approach is to represent gross profit as sales minus the cost of items sold. Also, indicate the operational income equal to the gross profit minus the selling and administrative expenses. Administrative, selling and manufacturing costs are all separated into three categories by absorption costing. Absorption costing is not as well understood as variable costing because of its financial statement limitations. But understanding how it can help management make decisions is very important.
Consequently, income before income taxes under variablecosting is $600 less than under absorption costing because morecosts are expensed during the period. If absorption costing is the method acceptable for financial reporting under GAAP, why would management prefer variable costing? Advocates of variable costing argue that the definition of fixed costs holds, and fixed manufacturing overhead costs will be incurred regardless of whether anything is actually produced. While companies use absorption costing for their financial statements, many also use variable costing for decision-making.
Conversely, ifinventories decreased, then sales exceeded production, and incomebefore income taxes is larger under variable costing than underabsorption costing. Absorption whats the difference between a sales order and an invoice costing is an easy and simple way of dealing with fixed overhead production costs. It is assuming that all cost types can allocate base on one overhead absorption rate.

